Article Catalog
Details of this chapter
This post will teach about the history of Linux.
Linux Background
Linux HistoryLearning to program the Linux system, you may be asking where did Linux come from? How did it evolve? Here is a brief history of the development of Linux. To talk about Linux, you have to start with UNIX.
History of UNIX
In 1968, a number of researchers from General Electric, Bell Labs, and MIT developed a special operating system called Multics, which synthesized a number of new concepts in multitasking file management and user connectivity.In 1969-1970, Ken Tompson and Dennis Ritchie, researchers at AT&T's Bell Labs, developed the UINX system based on the adoption of many Multics features. It ran on small machines and met the system's requirements for a research environment. From its inception, UNIX was a valuable, efficient, multi-user and multi-tasking operating system.UNIX began as a way to meet individual design needs and grew into a standard software product supported by many different developers.The first UNIX version was given free to the computer science departments of many leading universities.In 1972, Bell Labs began distributing a commercial version and licensed the system to various users, one of which was the Computer Science Department at the University of California, Berkeley. Berkeley added many new features to the system that later became the standard.In 1975 Berkeley released its own version of UNIX under the BSD division, and the BSD version of UNIX became a major competitor to the AT&T Bell Labs version, while other independently developed versions of UNIX began to sprout.In 1980 Microsoft developed a version of UNIX for the PC called Xenix.AT&T released the first commercial version. It was called System III and was later replaced by System V, which became a well-supported commercial software product.Meanwhile the BSD version of UNIX continued to evolve, and in the late 1970s BSD UNIX became the basis for scientific projects at the Department of Defense's high-tech research facilities. As a result, Berkeley released a valid version called BSD Release 4.2.It includes an advanced file manager and networking features based on the TCP/IP network protocol. TCP/IP is now used by the Internet.BSD Release 4.2 is used by many vendors, such as SUN Microsystem.The emergence of different versions of UNIX led to the need for UNIX standards, and software developers did not know which versions were appropriate for their programs to run on.By the mid-1980s, two competing standards emerged, one based on the AT&T version of UNIX and the other on the BSD version. In today's bookstores you can find books for each of these two different versions of UNIX, some for System V and others focused on BSD UNIX.AT&T created a new organization called the UNIX Systems Laboratory, whose role was to synthesize the different versions of UNIX and focus on the development of a standard system.In 1991, the UNIX Consolidation Laboratory combined all the features of System V Release 3, SUN OS, and Xenix and released System V Release 4. In order to compete with System V Release 4, a number of other companies, such as IBM and the Hewlett-Packard Open Software Foundation (OSF), went on to produce their own standard versions of UNIX, followed by two standard commercial versions, OSF Version and System Release 4. In order to compete with System V Release 4, some other companies, such as IBM and HP Open Software Foundation (OSF), went on to produce their own versions of the UNIX standard, and two commercial versions of the standard, OSF Release and System Release 4, emerged.In 1993, AT&T resold its UNIX to Novell, and UNIX Systems Labs became part of Novell's UNIX Systems Group.Novell released its own version of UNIX, UNIXWare, based on System V Release 4, which could be linked to Novell's Netware system. SUN had integrated System V Release 4 into its SUN OS, releasing Solaris, and the graphical user interfaces used by the two competing UNIXes, one called Motif and the other called Openlook, had been merged into a new workbench standard called the Common Platform Environment (CDE).
History of Linux
preambleOn October 5, 1991, Linus Benedict Torvalds, a graduate student at the University of Helsinki, announced in a Usenet newsgroup (comp.os.minix) that he had compiled a small UNIX-like operating system called Linux.The new operating system was inspired by another small UNIX operating system –Minix, which was developed by a teacher named Andrew S Tanenbaum. Read. One might assume that the system being released is Linux version 0.01, but this is not the case. The real Linux 0.01 was not released because 0.01 was not practical, and Linus only made the source code for this version available on the first Linux FTP site (ftp://nic.funet.fi).
The version of Linux Torvalds released on October 5 is called version 0.02, and it is capable of running the GNU Bourne Again Shell (bash) and the GNU C Compiler (gcc), as well as a handful of other languages.Torvalds had no idea that an operating system he envisioned targeting advanced hobbyists and hackers had been created. The operating system he envisioned for advanced hobbyists and hackers was already in place, and it became known as Linux;Linux was released with version 0.02, then 0.03 and then jumped to 0.10. Because more and more programmers all over the world are starting to develop Linux, it has reached version 0.95. This means that the time is not far away when exactly version 1.0 will be announced. The official version 1.0 was announced in 1994
Introduction to computers
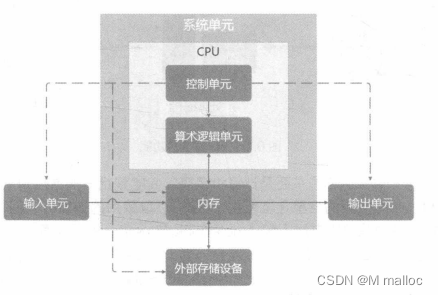
A great tool for the computer-assisted human brainNowadays, people almost all the time will not touch the computer, whether it is a desktop computer, laptop, tablet or smartphone and other such things are considered computers. Although so much contact, however, you understand what components inside the computer? In the case of a desktop computer, what components are inside the chassis of a computer? In what ways can different computers be used? What are some of the electrical appliances around you that are What about the ones that contain computer related components? Here we will talk about these things. The so-called computer is a kind of computer, and the computer is actually: accept user input commands and data, by the central processing unit of arithmetic and logic unit operation processing, produce or store into useful information. Therefore, as long as there is an input device (whether it is a keyboard or touch screen) and output device (such as a computer screen or directly from the printer to print out ), so that you can enter data to make the machine to produce information, that is a computer.
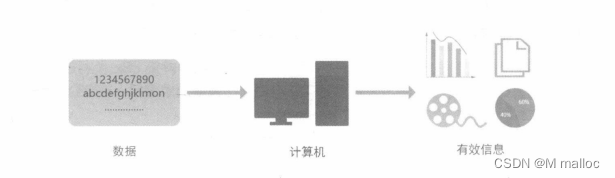
The diagram above shows the functions of a computer
The five major building blocks of a computer
We will know that computers are actually made up of several units, including input units, output units, control units inside the CPU, arithmetic logic units and memory.
How to consolidate learning
Tip: In the process of learning, we need to think on our own first and read more books by the big boys, as the saying goes, books are the ladder of human progress!
Summary of this article
Well, today’s share here on the end of it, I love you M malloc hope to help you Oh, the last don’t forget to triple la!